Eid-ul-Adha, commonly known as Bakrid, is a highly significant and emotional festival in Islam. This festival symbolizes sacrifice, dedication, and unwavering commitment to God. In 2025, it will be celebrated on different days in India and Saudi Arabia. In India, Bakrid will be observed on June 7th, 2025 (Saturday), while in Saudi Arabia, it will be celebrated on June 6th, 2025 (Friday).
Determining the Date of Bakrid: Lunar Calculations
According to the Islamic calendar, or Hijri calendar, Eid-ul-Adha is celebrated on the 10th day of the month of Dhul Hijjah. Since the Hijri calendar is based on the lunar cycle, the date of Eid-ul-Adha varies each year. In Saudi Arabia, the Dhul Hijjah crescent moon was sighted on the evening of May 27th, 2025, marking the beginning of the Islamic month on May 28th. Consequently, Eid-ul-Adha was determined to be on June 6th in Saudi Arabia.
Meanwhile, in India, the sighting of the crescent moon was confirmed on the evening of May 28th, leading to the first day of Dhul Hijjah being observed on May 29th. Based on this, Eid-ul-Adha will be celebrated on June 7th, 2025, in India. This one-day difference arises because the moon sighting tradition in India is localized, whereas Saudi Arabia makes a centralized announcement.
History and Religious Background of Bakrid

The origins of Bakrid are linked to a historical and faith-inspiring event. According to Islamic belief, Prophet Ibrahim (peace be upon him), upon God's command, resolved to sacrifice his son, Ismail. This was a test of faith. As he was about to offer his son, God, pleased with his devotion, sent a lamb in Ismail's place, which was sacrificed instead. Since then, this day has symbolized sacrifice and dedication to God.
The Significance of Qurbani and its Social Message
The central element of Bakrid is Qurbani, or sacrifice. On this day, Muslims sacrifice animals, typically goats, sheep, camels, or cows, which is a symbolic act. The purpose is to demonstrate a willingness to sacrifice everything for the sake of God. The meat from the sacrificed animal is divided into three parts:
- The first portion is given to the poor and needy.
- The second portion is shared among relatives and friends.
- The third portion is kept for the family.
This practice aims not only to uphold religious tradition but also to promote social equality, compassion, and service.
The Deep Connection Between Hajj and Bakrid
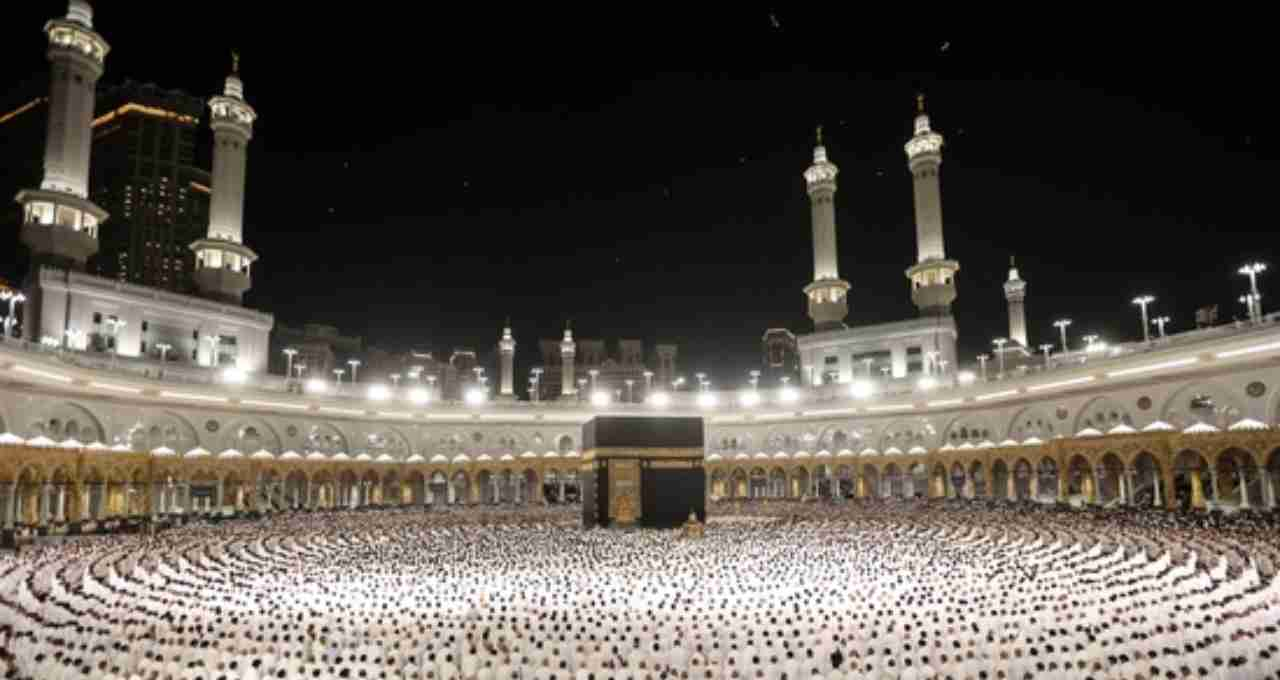

Another crucial aspect of Eid-ul-Adha is that it marks the culmination of Hajj. Hajj is the fifth pillar of Islam, and every able-bodied Muslim is expected to perform this pilgrimage at least once in their lifetime. On the final day of Hajj in Mina, Muslims perform the ritual of stoning the devil, followed by the sacrifice of an animal.
Markets become bustling in the days leading up to Eid-ul-Adha. People buy new clothes, prepare sweets, and special dishes. The purchase, care, and adornment of sacrificial animals bring a unique excitement. Special prayers are offered in the morning, followed by the sacrifice.
Bakrid is not merely a religious festival; it conveys a social and humanitarian message – that sacrifice and service are paramount. This festival teaches us to set aside our desires, self-interest, and ego to serve others.