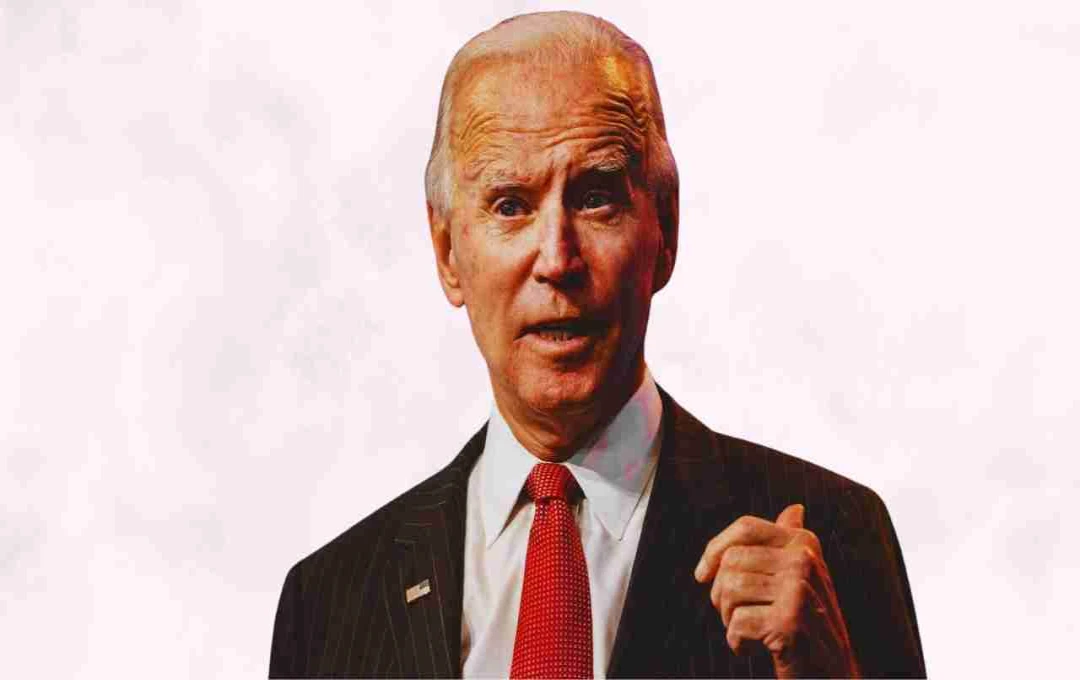
News of former US President Joe Biden's prostate cancer diagnosis has reignited global discussion surrounding this disease. Reports indicate the cancer has reached an advanced stage and metastasized to his bones. This is not only a cause for concern but also a stark warning to all men: prostate cancer should not be taken lightly.
What is Prostate Cancer?
Prostate cancer is a common yet serious disease affecting men. The prostate is a small gland playing a crucial role in the male reproductive system. Located just below the bladder, it produces a fluid that nourishes and protects sperm. Prostate cancer occurs when cells in this gland grow abnormally and uncontrollably.

This disease is typically associated with aging, with higher incidence rates in men over 60. However, cases are increasingly being observed in men under 50. A major problem is that initial symptoms are often mild or absent, allowing the cancer to spread undetected. This is why it's often called a "silent killer"—by the time symptoms become apparent, the disease may be advanced. Therefore, timely screening and vigilance are crucial.
Why is Joe Biden's Case a Warning?
A recent official statement revealed that former President Biden's prostate cancer is in a severe, advanced stage. At this stage, cancer cells have spread to his bones, a condition known as metastatic prostate cancer, which is particularly challenging and dangerous to treat.
Doctors indicate that at this stage, treatment may involve hormone therapy, chemotherapy, and medications targeting bone-related effects. Treatment success depends on the cancer's growth rate and the patient's age and overall health. Biden's case highlights the often-late diagnosis of this disease, emphasizing the importance of timely screening and treatment.
Key Symptoms of Prostate Cancer Not to Ignore
Early detection is vital for effective prostate cancer treatment. Several key symptoms warrant attention:
Urinary Problems: The most common symptom is difficulty urinating. This can include burning or pain during urination, frequent urination (especially at night), interrupted urine flow, or a weak urine stream. Blood in urine or semen is a serious warning sign.
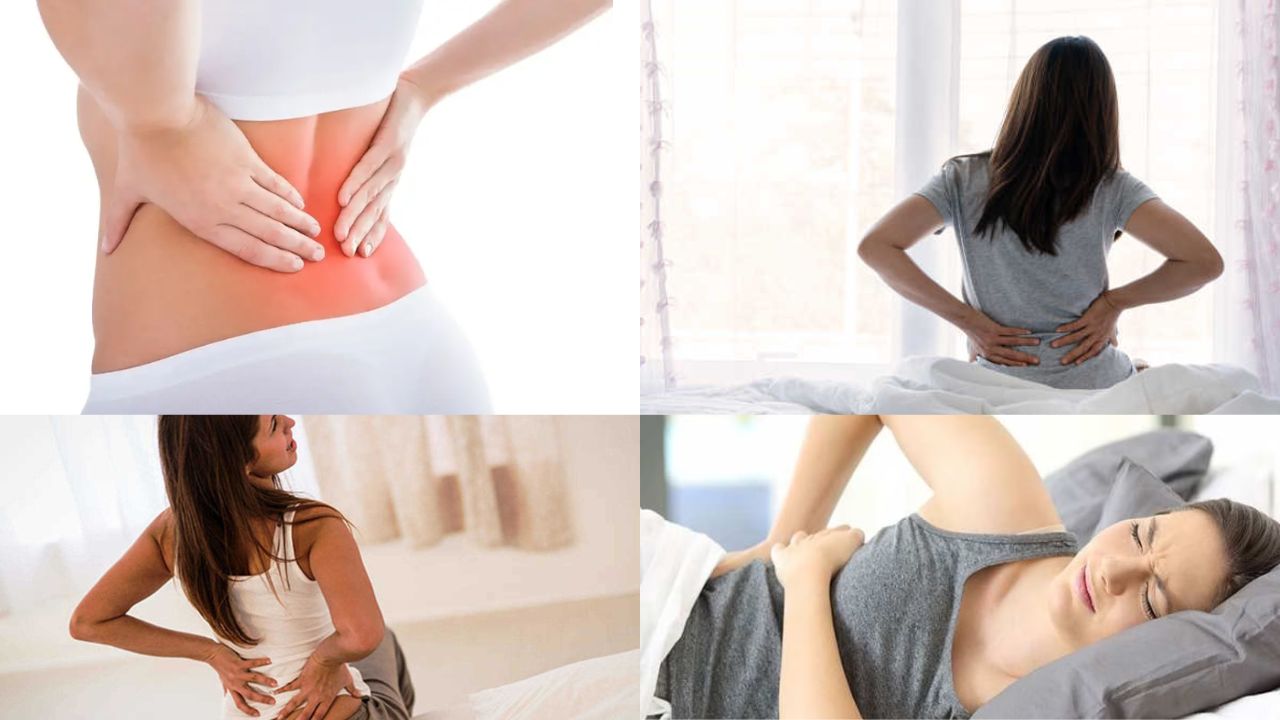
Bone Pain: If the cancer metastasizes to the bones, it causes sharp, persistent pain in the lower back, hips, or pelvic area. This pain is often unrelieved by rest or medication, significantly impacting daily life.
Fatigue and Weakness: Prostate cancer can drain energy levels. Patients may experience unexplained fatigue, weakness, and dizziness, often due to weakened immunity.
Sudden Weight Loss: Unexplained weight loss, without dietary changes or increased exercise, is a serious concern and could indicate underlying health issues, including cancer.
Erectile Dysfunction: Prostate cancer can cause sexual issues, particularly erectile dysfunction. Pressure from the cancer on the gland can lead to difficulties with sexual intercourse.
How is Prostate Cancer Detected?
Persistent prostate cancer symptoms necessitate immediate medical attention. Several tests aid in diagnosis:
PSA Test (Prostate-Specific Antigen Test): This blood test measures the level of PSA, a protein produced by the prostate gland. Elevated PSA levels may indicate prostate cancer or inflammation. It’s a common initial screening test guiding further procedures.
Digital Rectal Exam (DRE): A doctor inserts a finger into the rectum to examine the prostate gland, checking for abnormalities like lumps or hardening. It's a simple, quick test providing preliminary information.
MRI and Biopsy: If PSA tests and DRE raise concerns, MRI scans and biopsies follow. MRI provides detailed images of the prostate and surrounding organs. A biopsy involves taking a small tissue sample from the prostate for examination to confirm cancer and its severity. These are crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
How is Prostate Cancer Treated?
Prostate cancer treatment varies depending on the stage, patient age, and overall health. Timely treatment can control the disease.
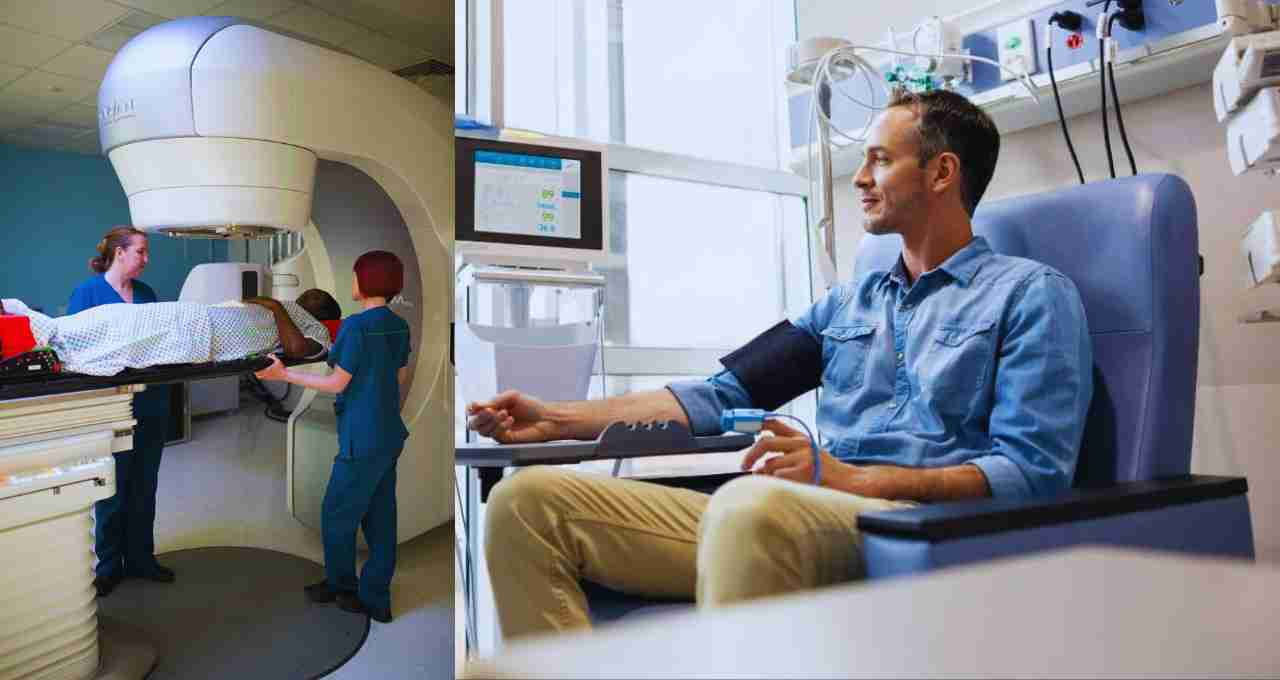
Surgery (Prostatectomy): If cancer is in the early stages and confined to the prostate, surgery may be recommended. This involves removing all or part of the affected prostate gland, potentially eliminating the cancer. Post-surgical urinary or sexual issues are possible, but modern techniques mitigate these risks.
Radiation Therapy: Radiation therapy uses controlled doses of high-energy radiation to destroy cancer cells. This is a suitable option for patients who cannot undergo surgery or prefer to avoid it. Common side effects include fatigue and skin irritation.
Hormone Therapy: Prostate cancer growth relies on testosterone. Hormone therapy reduces testosterone levels to halt cancer growth. It can be used alone or in conjunction with surgery and radiation, particularly managing advanced stages.
Chemotherapy: If the cancer is rapidly spreading or has reached other body parts, chemotherapy is used. Special medications kill cancer cells, slowing growth and improving the patient's quality of life. Side effects like hair loss, nausea, and weakness can occur.
Bone-Targeted Therapy: When prostate cancer spreads to the bones, bone-targeted therapy is employed. Medications reduce the cancer's effects on the bones, strengthening them, relieving pain, and reducing fracture risk.
Easy Ways to Prevent Prostate Cancer
- While complete prevention is difficult, adopting healthy habits can reduce risk.
- Consume a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and fiber to boost immunity and lower cancer risk.
- Limit red meat and fast food consumption, as they may increase prostate cancer risk.
- Daily exercise (at least 30 minutes of light activity) maintains overall health and aids in fighting cancer.
- Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption are harmful and increase cancer risk; cessation is crucial.
Men over 50 should undergo regular check-ups to detect and treat any issues promptly. Biden's case underscores the dangers of late-stage prostate cancer, a disease that gradually weakens the body. Ignoring symptoms and delaying proper diagnosis and treatment should be avoided.