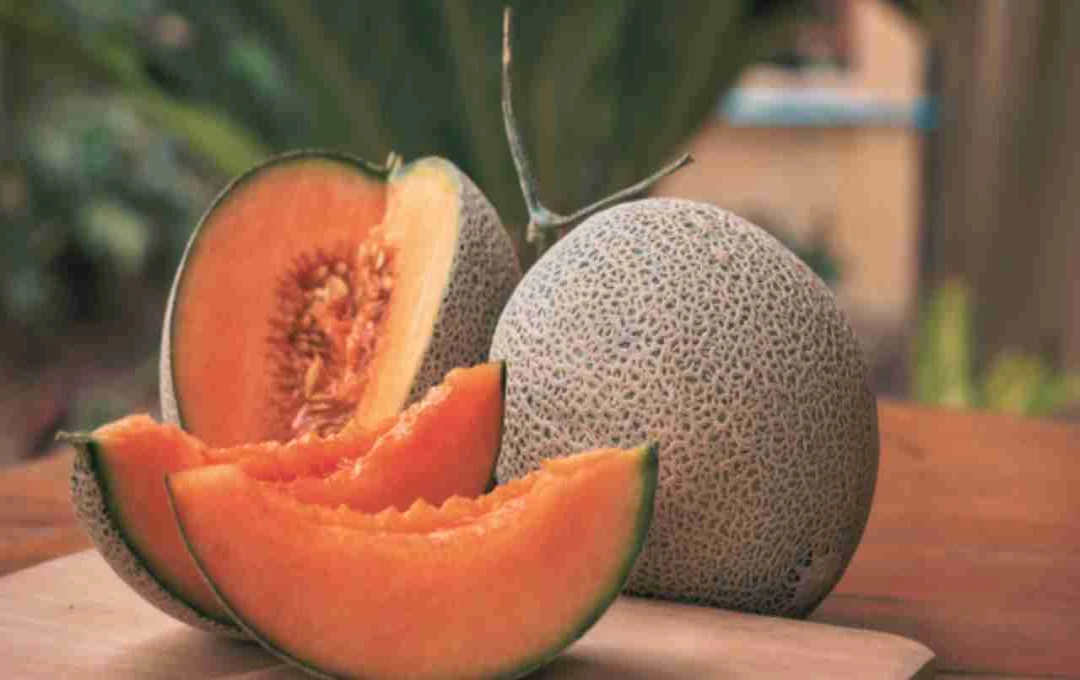
Cantaloupe, a refreshing and cooling fruit, is a summer favorite for many. Its sweet taste and high water content provide relief from the heat. Cantaloupe is rich in nutrients, containing Vitamin C, Vitamin A, fiber, and potassium, all beneficial for health. However, it's crucial to understand that cantaloupe isn't universally beneficial; it can be detrimental for individuals with certain health conditions.
For Diabetics – The Sweet Taste Can Be Risky
Cantaloupe's sweetness stems from its high fructose content. Consumption by diabetics can lead to a rapid increase in blood sugar levels. Cantaloupe has a moderately high glycemic index, meaning it digests quickly and elevates blood sugar. Therefore, diabetics should consume it cautiously.
What to Do?
Diabetics who wish to consume cantaloupe should do so in moderation. Pairing it with protein or fiber-rich foods, like nuts or yogurt, can help moderate the blood sugar spike. Fruits with lower glycemic indices, such as guava, berries, or oranges, are preferable for better blood sugar control. Always consult a doctor before making dietary changes.
For Kidney Patients – High Potassium Can Be Harmful
Cantaloupe is a good source of potassium, an essential electrolyte beneficial for heart health. However, excessive potassium can be harmful for individuals with kidney dysfunction. Weakened kidneys struggle to eliminate potassium, leading to its buildup, potentially causing irregular heartbeat and serious health problems.
What to Do?
Individuals with kidney problems should avoid cantaloupe without consulting their doctor. Kidney patients should limit their intake of potassium-rich fruits. Apples, blueberries, and grapes, which are lower in potassium, are suitable alternatives. Maintain a balanced diet in consultation with a physician.
For Individuals with Cold, Cough, and Sore Throat
Cantaloupe's cooling nature provides relief in summer. However, it may be detrimental for those frequently suffering from colds, sore throats, or inflammation. It can increase mucus production, worsening coughs and sneezes.

What to Do?
Those with colds or sore throats should avoid cold fruits like cantaloupe. Warmer fruits like papaya or guava are better alternatives. Warm water or turmeric milk can soothe the throat and combat infection.
For Individuals with Allergies and Sensitive Stomachs – Risk of Allergic Reactions and Indigestion
Some individuals may experience cantaloupe allergies, which can sometimes be severe. Allergic symptoms include itching, rashes, swelling, breathing difficulties, or vomiting. People with weak or sensitive digestive systems might experience stomach pain, gas, indigestion, or cramps after consuming cantaloupe, especially if eaten cold or on an empty stomach.
What to Do?
If you suspect a cantaloupe allergy, consult a doctor or undergo allergy testing. Individuals with sensitive stomachs should opt for easily digestible foods like ripe bananas, applesauce, or boiled potatoes. Consume cantaloupe at room temperature, not chilled.
For Individuals with Diarrhea or Upset Stomach – High Water Content Can Worsen the Condition
Cantaloupe, being about 90% water, offers cooling effects. However, it can worsen diarrhea or upset stomachs. The high water content can loosen stools, prolonging diarrhea. It can also cause electrolyte imbalance, leading to weakness and dehydration.
What to Do?

In case of diarrhea or an upset stomach, consume a bland, easily digestible diet including bananas, rice, soup, and yogurt. Avoid cold and watery foods, including cantaloupe. Refrain from such fruits until recovery and drink plenty of lukewarm water to prevent dehydration.
Alternative Fruits to Cantaloupe
If you cannot or prefer not to eat cantaloupe, several other healthy and readily available fruits offer excellent nutritional benefits. These fruits are not only tasty but also provide essential nutrients to your body.
Apples: Apples are a healthy fruit, particularly beneficial for diabetics. Their high fiber content improves digestion and regulates blood sugar. Apples promote healthy digestion and heart health.
Oranges: Oranges are rich in Vitamin C, boosting immunity. They offer a cooling effect, but less intense than cantaloupe, making them suitable for those with colds. Orange juice is also refreshing in summer.
Guava: Guava is high in fiber, promoting healthy digestion. It reduces inflammation and helps control blood pressure. It alleviates constipation and aids in weight management.
Bananas: Bananas are excellent for digestion. They contain elements that reduce heartburn and acidity. They also provide instant energy, making them ideal for a morning or evening snack. Bananas are beneficial for both children and the elderly.
Mangoes: Mangoes are a summer favorite. They contain Vitamins A and C, beneficial for skin and eyes. They offer a cooling effect and provide quick energy. Mangoes come in various sweet and tangy varieties.
Cantaloupe, while a delicious and refreshing fruit, isn't safe for everyone. Its consumption can be detrimental rather than beneficial in specific health conditions. Understanding your health status and consulting a doctor or dietitian before incorporating it into your diet is essential.