India launched Operation Sindur, a targeted cross-border strike against terrorist bases in Pakistan and Pakistan-occupied Kashmir (PoK). This was India's largest cross-border precision strike since the Balakot operation in 2019.
New Delhi: The Indian Army conducted a swift and precise operation, codenamed Operation Sindur, targeting terrorist camps in Pakistan and PoK. This operation marks India's largest cross-border strike since Balakot in 2019. Indian forces utilized advanced weaponry, resulting in significant destruction of terrorist infrastructure.
The operation employed weapons such as SCALP cruise missiles, Hammer precision bombs, and loitering munitions. Operation Sindur not only neutralized terrorist bases in Pakistan but also served as a b message to the world that India is fully prepared to take decisive action against terrorism.
Operation Sindur: Utilization of Advanced Weapons
Operation Sindur saw the Indian military deploy state-of-the-art weapons and technology. Key weapons included SCALP cruise missiles, Hammer precision bombs, and loitering munitions.
1. SCALP Cruise Missile (SCALP-EG/Storm Shadow)
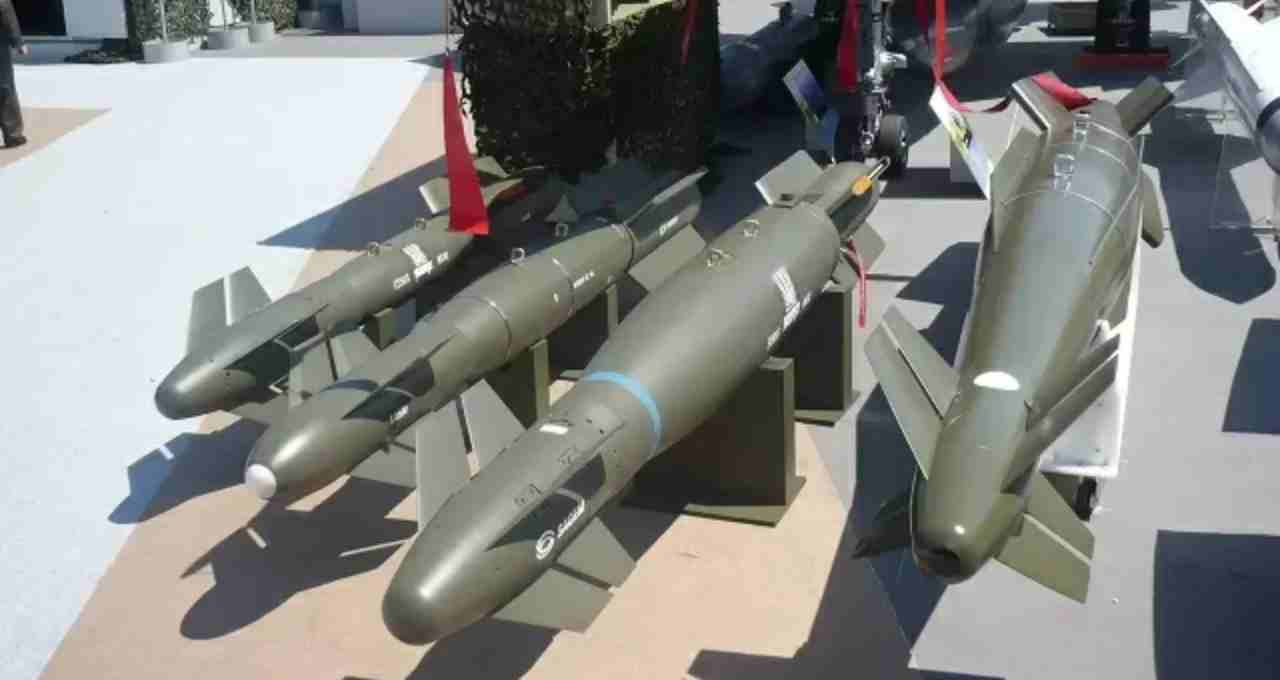

This is a long-range, low-visibility air-to-ground cruise missile jointly developed by France and Britain. The Indian Air Force's 36 Rafale fighter jets are equipped with this missile.
SCALP Features
- Range: 250-560 km (depending on launch altitude)
- Speed: Subsonic, Mach 0.8 (approximately 1000 km/h)
- Weight: Approximately 1300 kg
- Guidance System: GPS and inertial navigation
- Infrared Seeker: Terminal guidance based on the target's thermal signature
- Terrain Referencing Navigation: Flight based on terrain features, aiding in radar evasion.
- Flight Altitude: Low-altitude flight between 100 and 130 feet, enabling radar evasion.
2. Hammer (Highly Agile Modular Munition Extended Range)
Hammer is a smart bomb specifically designed to target hardened structures such as bunkers and multi-story buildings. It can engage targets up to 50-70 kilometers away and features a precision guidance system ensuring accurate impact.
3. Loitering Munition
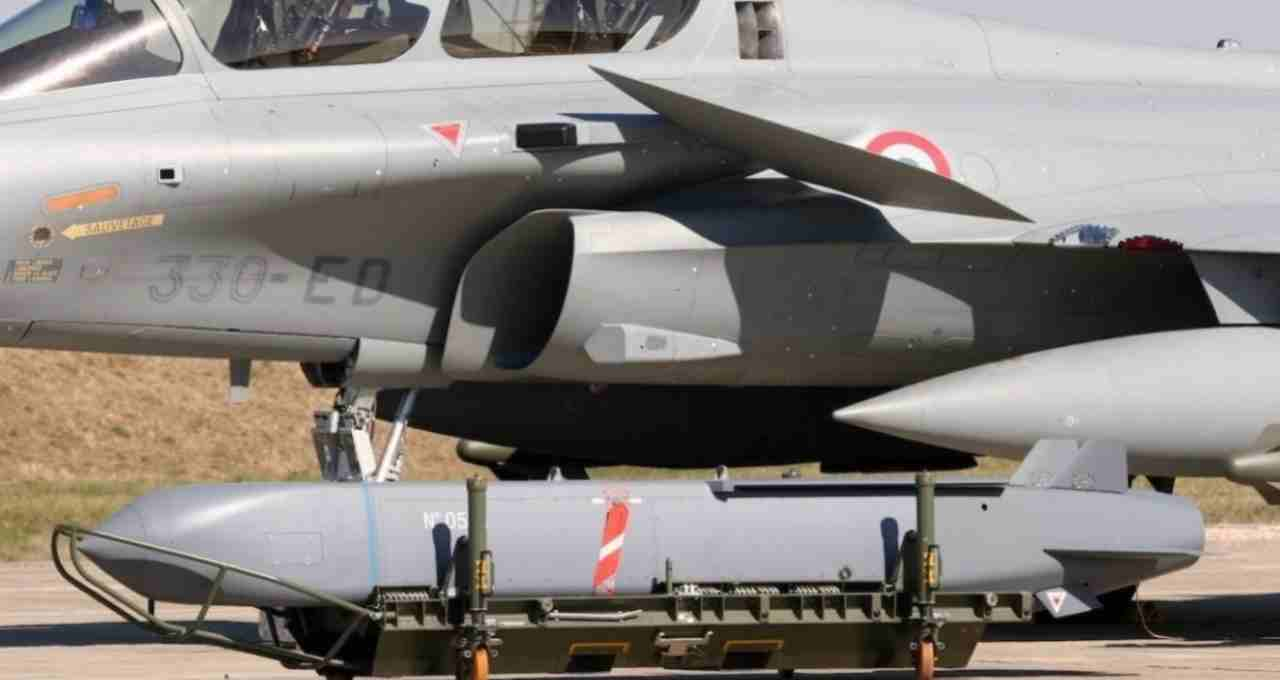

Also known as suicide drones, this unmanned aerial weapon loiters above its target before striking. Once a target is acquired, it destroys its objective. It is a precise and effective weapon, highly successful in eliminating its targets.
Operation Sindur: Targeting Terrorist Bases in Pakistan
During Operation Sindur, the Indian Army targeted nine major locations; four in Pakistan and five in PoK. All locations were specifically selected to target bases of terrorist groups involved in spreading terrorism in India.
- Muridke: A major Lashkar-e-Taiba camp located 30 kilometers from the international border, used for infiltration into India.
- Gulpur: A terrorist base located 35 kilometers from the LOC near Poonch-Rajouri, used for cross-border terrorist training.
- Lashkar Camp Sawai: Located in the Tangdhar sector of PoK, approximately 30 kilometers from the Indian border.
- Bilal Camp: A Jaish-e-Mohammed launchpad used for cross-border infiltration, also targeted under Operation Sindur.
- Kotli: A Lashkar-e-Taiba camp 15 kilometers from the LOC, used for training terrorists for infiltration into Indian territory.
- Barnala Camp: Located 10 kilometers from the LOC, where Hizbul Mujahideen terrorists were trained.
- Sarjal Camp: A Jaish-e-Mohammed training center 8 kilometers from the international border, used for infiltration into India.
- Mehmuna Camp: A Hizbul Mujahideen training camp located 15 kilometers from the international border.

Ministry of Defence Statement
The Ministry of Defence clarified that no Pakistani military installations were targeted. All strikes were exclusively against facilities used by terrorist groups as operational bases. According to the ministry, the action was purely anti-terrorism and did not aim to harm innocent civilians.
Following Operation Sindur, reactions emerged from Pakistan, China, and Turkey. Pakistan protested, citing violation of its territorial sovereignty. China expressed concern and appealed for peace between the two nations. Israel and the United States, however, supported India's right to self-defense and commended its actions against terrorism.