Following the Pulwama terror attack, tensions between India and Pakistan once again escalated to a critical point. In response to the attack, India launched ‘Operation Sundar’, carrying out airstrikes on nine terrorist camps located within Pakistan's borders, effectively neutralizing them.
India S-400 vs China HQ9: The Pulwama attack brought India and Pakistan to the brink. India's response was not only swift but also decisive, catching the world's attention. Under Operation Sundar, the Indian Army destroyed nine terrorist camps, ranging from Pakistan-occupied Kashmir (PoK) to deep within Pakistan. Pakistan attempted a counter-attack, but India's S-400 Triumf system, known as 'Sudarshan Chakra', thwarted their efforts. Furthermore, Pakistan's HQ-9 air defense system, based on Chinese technology, was also destroyed during the engagement.
The question arises: which system, India's S-400 or Pakistan's HQ-9, is more powerful? Can the HQ-9 truly compete with the S-400? Let's analyze the technical specifications to determine which system holds the upper hand on the battlefield.
India's S-400 Sudarshan Chakra: A Warrior Unleashing Aerial Destruction

The S-400 Triumf system, imported from Russia and named 'Sudarshan Chakra' by India, is designed to meet the demands of modern warfare.
Key Features
- Range: The S-400 can engage enemy targets up to 400 km.
- Radar Capability: It can detect airborne threats up to 600 km away.
- Target Tracking: Capable of tracking 100 targets simultaneously.
- Attack Capability: Can simultaneously destroy 36 targets.
- Guidance System: Employs active and semi-active radar, along with Track via Missile (TVM) technology.
India has strategically deployed the S-400 in crucial locations, including Delhi, Punjab, Rajasthan, Jammu & Kashmir, and the northeastern borders.
Pakistan's HQ-9: Chinese Technology, but Weak in Impact
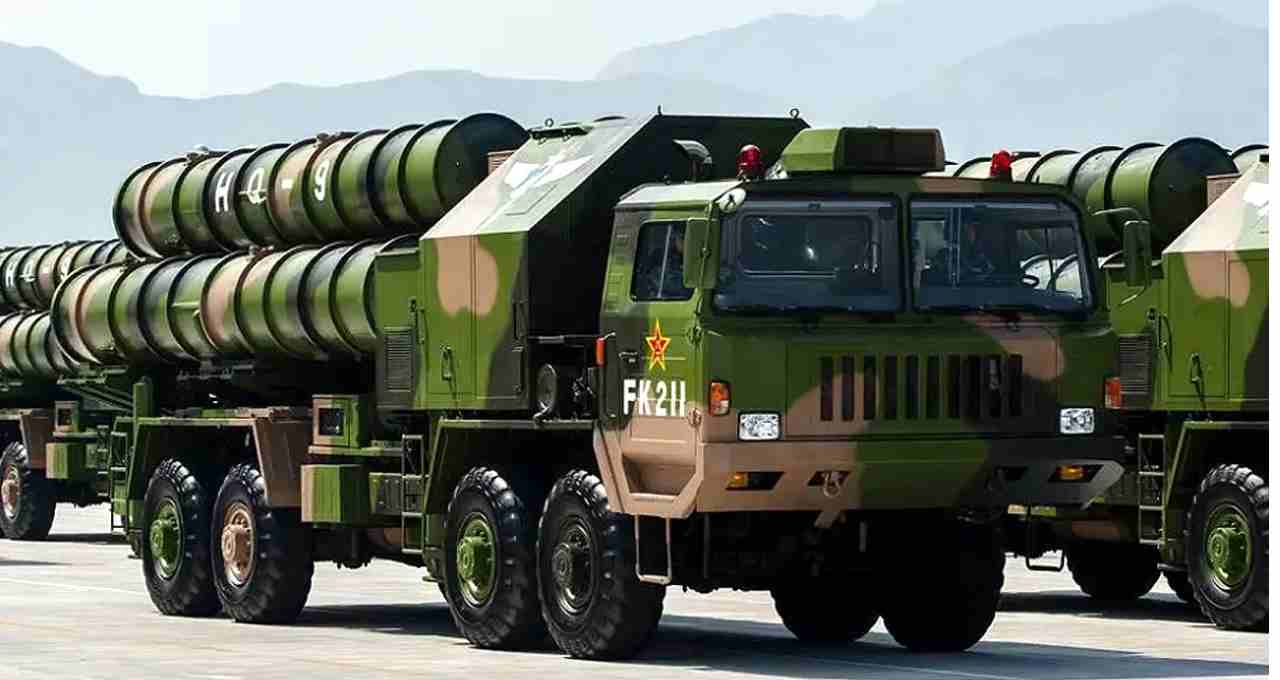

The HQ-9 is a long-range surface-to-air missile system manufactured in China, adopted by Pakistan in recent years. This system is based on China's S-300 and Russian technology.
Key Features
- Range: The HQ-9 has a limited engagement range of 125 to 250 km.
- Radar Detection: Can detect targets within a range of 150-200 km.
- Target Tracking: Capable of tracking 100 targets simultaneously, but can only engage 8-10 targets.
- Guidance System: Based on semi-active radar and TVM technology.
The recent conflict exposed the shortcomings of Pakistan's air defense capabilities, with the HQ-9 rendered ineffective within minutes by India's precision strikes and the countermeasures from the S-400.
S-400 vs HQ-9

| Feature | S-400 (India) | HQ-9 (Pakistan) |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum Targets Tracked | 100 | 100 |
| Maximum Targets Engaged | 36 | 8-10 |
| Radar Detection Range | 600 km | 150-200 km |
| Engagement Range | 40-400 km | 25-125 km |
| Missile Guidance | Active/Semi-active Radar, TVM | Semi-active Radar, TVM |
| Combat Tested | Yes | Yes |
This recent clash clearly demonstrates that simply acquiring missile systems is insufficient; strategic deployment and intelligence are equally crucial. India's S-400, capable of detecting targets via radar and eliminating threats from long range, proved superior to Pakistan's HQ-9, which suffered from limited range and attack capacity.